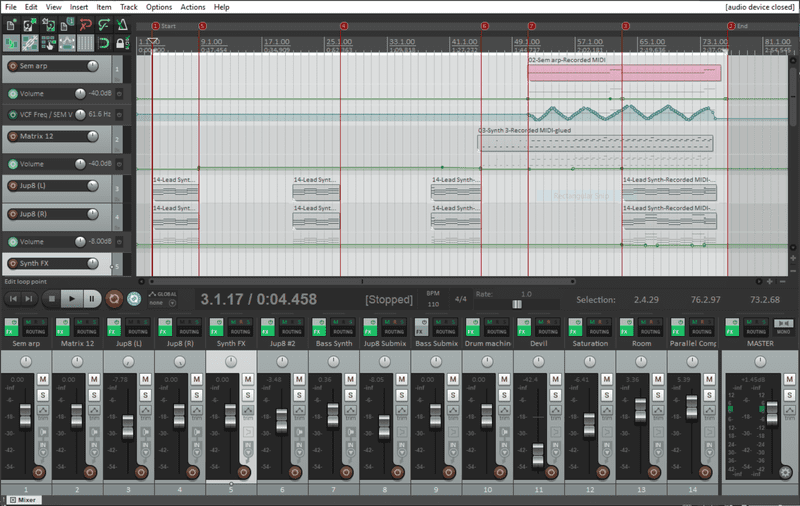
Mastering the Art of Synth Mixing in Your DAW: A Practical Guide
Learning how to mix synths in digital audio workstations (DAWs) can be daunting, especially for music lovers starting their journey. At theautonomics.com, we understand this challenge. This comprehensive guide provides practical advice and assistance to help you confidently blend your synth sounds, creating rich and professional-sounding mixes. This article will explore various techniques for how to mix synths in digital audio workstations, ensuring your synth tracks shine.
Explore
- 1 Understanding Your Synth Sounds
- 2 EQ: Sculpting Your Synth Sounds
- 3 Compression: Controlling Dynamics
- 4 Effects: Adding Depth and Character
- 5 Panning and Stereo Width: Creating Space in the Stereo Field
- 6 Automation: Adding Movement and Interest
- 7 Mastering the Art of Subtractive Mixing
- 8 How to Mix Synths in Digital Audio Workstations: A Summary of Key Techniques
- 9 Final Thoughts: Achieving a Powerful Synth Mix
Understanding Your Synth Sounds
Before diving into the mixing process, it’s crucial to understand the individual characteristics of your synth sounds. How to mix synths in digital audio workstations effectively begins with knowing your source material. Each synth has its own unique sonic fingerprint, shaped by its oscillators, filters, envelopes, and effects.
Analyzing the Frequency Spectrum
Pay close attention to the frequency content of each synth. Some synths might be bass-heavy, others mid-range focused, and some might occupy the higher frequencies. Identifying these frequency ranges is fundamental to how to mix synths in digital audio workstations successfully, as it helps you avoid muddiness and clashing frequencies.
Identifying Transient and Sustain
Observe how each synth behaves in terms of its attack and decay. Synths with fast attacks and short decays might need different EQ and compression techniques compared to those with slow attacks and long sustains. This understanding is essential when you’re learning how to mix synths in digital audio workstations.
EQ: Sculpting Your Synth Sounds
EQ is a cornerstone of how to mix synths in digital audio workstations. It allows you to shape the frequency response of your synths, removing unwanted muddiness and highlighting desirable characteristics.
High-Pass Filtering

Start by applying high-pass filters (HPF) to your synths. This removes low-frequency rumble and mud that can clutter your mix. A good starting point is around 80-150Hz, but adjust this based on the specific synth sound. How to mix synths in digital audio workstations efficiently often involves judicious use of HPFs.
Low-Pass Filtering
Conversely, low-pass filters (LPF) can be used to tame harsh high frequencies. This is particularly useful for synths with bright, piercing tones. Experiment to find the sweet spot that retains clarity without sounding harsh. This is another critical aspect of how to mix synths in digital audio workstations.
Notch Filtering
Notch filters are designed to target specific frequencies, often used to remove resonant peaks or unwanted noises. Careful use of notch filters can significantly improve the clarity and definition of your synth sounds, contributing to the overall success of how to mix synths in digital audio workstations.
Compression: Controlling Dynamics
Compression helps control the dynamic range of your synths, making them sit better in the mix.
Parallel Compression
Parallel compression involves sending a copy of your synth track to an aux channel with a compressor. This allows you to add punch and sustain without overly squashing the dynamics of the original signal. This technique is invaluable when learning how to mix synths in digital audio workstations.
Bus Compression
Bus compression involves compressing multiple synth tracks together on a group or bus channel. This creates cohesion and glue between the synths, resulting in a more unified sound. This is often a crucial part of how to mix synths in digital audio workstations for a polished result.
Transient Shaping
Some compressors offer transient shaping capabilities, allowing you to control the attack and release of your synth sounds. This can add punch or smoothness, depending on your needs, and is an advanced technique in how to mix synths in digital audio workstations.
Effects: Adding Depth and Character
Effects can add depth, width, and character to your synth sounds.
Reverb: Creating Space
Reverb adds a sense of space and ambience to your synths. Use reverb sparingly to avoid muddying the mix. Experiment with different reverb types and decay times to find what works best for each synth. Understanding reverb is key when learning how to mix synths in digital audio workstations.
Delay: Adding Rhythm
Delay adds rhythmic interest and texture to your synths. Use short delays for rhythmic emphasis or longer delays for atmospheric effects. How to mix synths in digital audio workstations effectively often includes strategic delay placement.
Chorus: Widening the Sound
Chorus creates a thicker, wider sound by slightly detuning multiple copies of your synth. Use chorus sparingly to avoid phasing issues. How to mix synths in digital audio workstations involves balancing the use of chorus to avoid muddiness.
Distortion: Adding Grit
Distortion can add grit and edge to your synths. Use distortion sparingly to avoid harshness. Experiment with different distortion types and amounts to find what works best for each synth. Subtle distortion can greatly enhance how to mix synths in digital audio workstations.
Panning and Stereo Width: Creating Space in the Stereo Field
Proper panning and stereo width placement are essential for creating a spacious and engaging mix.
Panning Synths
Panning your synths across the stereo field can create a wider, more immersive sound. Avoid placing all your synths in the center, as this can lead to a cluttered mix. How to mix synths in digital audio workstations requires careful panning considerations.
Stereo Widening
Stereo widening effects can create a broader stereo image for your synths. Use stereo widening sparingly to avoid phasing issues. This technique is a valuable tool in how to mix synths in digital audio workstations.
Automation: Adding Movement and Interest
Automation allows you to change parameters of your synths and effects over time, adding movement and interest to your mix.
Filter Automation
Automating filter cutoff frequencies can create dynamic and evolving sounds. This is a powerful technique for adding interest to your synth lines. This is a crucial aspect of how to mix synths in digital audio workstations creatively.
Effect Automation
Automating reverb send levels or delay times can create subtle or dramatic changes in your synth sounds. How to mix synths in digital audio workstations effectively often incorporates automation techniques.
Mastering the Art of Subtractive Mixing
Subtractive mixing focuses on removing unwanted frequencies rather than adding effects. This is a powerful approach to how to mix synths in digital audio workstations cleanly.
Strategic EQ Cuts
Precise EQ cuts can eliminate muddiness and improve clarity, allowing your synth sounds to breathe. This is essential for how to mix synths in digital audio workstations for a professional sound.
Careful Compression
Subtle compression can control dynamics without squashing the life out of your synth sounds. Knowing how much compression to apply is a key skill in how to mix synths in digital audio workstations.
How to Mix Synths in Digital Audio Workstations: A Summary of Key Techniques
Successfully navigating how to mix synths in digital audio workstations hinges on a multifaceted approach. Understanding your synth sounds, employing EQ and compression effectively, utilizing effects judiciously, and implementing panning and automation strategically are all critical components. Remember, the goal is not to make each synth sound perfect in isolation, but to create a cohesive and engaging whole.
Final Thoughts: Achieving a Powerful Synth Mix
The journey of learning how to mix synths in digital audio workstations is a continuous process of experimentation and refinement. Don’t be afraid to experiment with different techniques and find what works best for your style and your specific tracks. By applying the principles outlined in this guide, you’ll be well on your way to creating powerful and impressive synth mixes that will captivate your listeners. Remember, consistent practice and a keen ear are your greatest allies in mastering this essential skill. The key to success in how to mix synths in digital audio workstations is patience, persistence, and a willingness to learn.